Degree:
A degree is a unit of angle measurement equal to 1/360 of a circle’s circumference.
Radian:
A radian is a unit of angle measurement that is the ratio of the circle arc cut off by an angle to the central angle.
Sine:
Sine on a unit circle is the “y” coordinate for any intersection between a standard angle and the circle.
Cosine:
Cosine on a unit circle is the “x” coordinate for any intersection between a standard angle and the circle.
Tangent:
The ratio of sine to cosine or, in a right triangle, is the ratio of the length of the opposite side to the length of the adjacent side.
Reference Angle:
A reference angle is the angle between 0 and 90 made with the x axis.
Form of a Trigonometric Function:
Trigonometric functions take the form 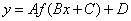 where A,B, C, and D are coefficients that change the characteristics of that trigonometric function.
where A,B, C, and D are coefficients that change the characteristics of that trigonometric function.
Graphs of Trigonometric Functions:
Graphs may be affected wildly as follows:
Stretching or compressing it along the x-axis
Stretching or compressing it along the y-axis
Moving it up or down along the y-axis

